Ceramic fiber module lining. At present, the lining structure of ceramic fiber used in heating furnaces in the petroleum refining and chemical industry is mainly composed of ceramic fiber modules and ceramic fiber blankets. The formation process of the composite lining structure is as follows:
- Clean and remove rust and anti-corrosion treatment of the furnace wall steel plate.
- Carry out the defense line according to design requirements and determine the position of anchor nails.
- Install the defense line position and weld anchor nails.
- Lay a ceramic fiber blanket as a backing insulation blanket and level it.
- Install the ceramic fiber module; the installation diagram is as follows:
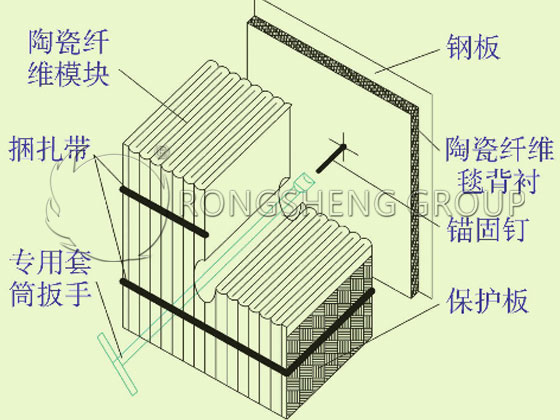
Reasons for the Sharp Shrinkage of Ceramic Fiber Modules
The high-aluminum ceramic fibers and zirconium-containing ceramic fibers commonly used in the lining of heating furnaces in oil refining and chemical plants are both glassy ceramic fibers, which will shrink under long-term high temperatures. This is determined by the properties of the ceramic fiber material itself. Microscopically, it is caused by the crystallization (crystallization) and grain growth of glassy ceramic fibers at high temperatures. Glass is formed by supercooling (rapid cooling) of the melt. This state is not the lowest energy state. It has a higher internal energy than the crystal and is a metastable state.
From a thermodynamic point of view, it has a tendency to spontaneously transform into a low-energy state, and the atoms can automatically rearrange; that is, it has a tendency to crystallize and transform into a crystalline state.
From a kinetic point of view, due to the high viscosity of glassy materials at room temperature, the diffusion and rearrangement speed of internal atoms is low, and the speed of transformation from glassy state to crystalline state is very slow, which makes it have great relative stability at room temperature and is also a stable state.
Glassy ceramic fibers have the characteristics of short-range order and long-range disorder. As the temperature rises, the viscosity of the fiber decreases, the atomic movement intensifies, the atomic diffusion and regular arrangement speed increase, and the long-range disorder turns into an ordered arrangement, that is, crystallization. The ordered regular rows are reduced, resulting in the volume shrinkage of a single ceramic fiber rod. Under the action of high temperature for a long time, the formed particles will grow, and the surface of the ceramic fiber rod will become uneven, that is, the diameter will shrink. Continuous diameter shrinkage will cause the length of the ceramic fiber to shorten, resulting in overall shrinkage.
Its shrinkage damage is shown in the following Figure.
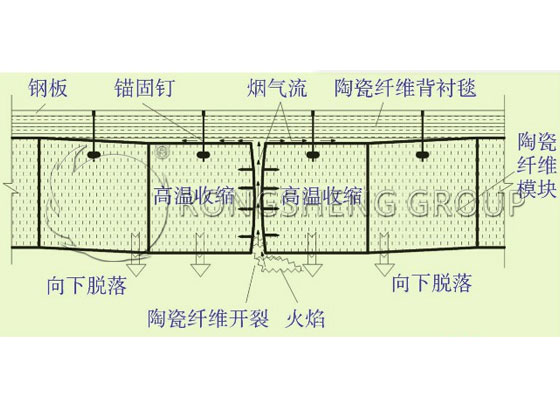
After macro-shrinkage occurs, the ceramic fiber furnace lining will crack and form gaps under the action of a long-term flame atmosphere. After the gap appears, the flame and airflow will take the opportunity to enter the gap, so that the ceramic fibers on both sides of the gap are directly in contact with the flame and airflow to become working. As time goes on, the ceramic fibers on the contact surface shrink and expand perpendicular to the contact surface, causing the gap to become larger and larger. In this way, more and more flame airflow will enter, and it will continue to spread and develop around. After contacting the anchor nail, the anchor nail will oxidize and corrode under the action of long-term high-temperature airflow, and eventually break, causing the ceramic fiber module to fall off. At the same time, the ceramic fiber backing also shrinks and powders, and then breaks and falls off, eventually causing the entire ceramic fiber furnace lining to be damaged and fall off.
What are the Precautions for Using Ceramic Fiber Blankets?
Ceramic fiber blankets, also known as aluminum silicate fiber blankets, are called ceramic fiber blankets because one of their main components is alumina, which is the main component of porcelain. So, what are the precautions for ceramic fiber blankets? Let’s first understand its characteristics!
Characteristics of ceramic fiber blankets
- High temperature resistance, the use temperature is as high as 1250° or above.
- Good thermal shock resistance.
- Has stable physical and chemical properties.

Precautions for using ceramic fiber blankets
- Before the construction of ceramic fiber blankets, the verticality and flatness of the base material must be determined.
- Do not mix the dried paste with water before use.
- The wall needs to be moistened in advance before construction, with no visible water as the standard.
- The mixed putty should be used up within 5 hours.
- Do not construct outside 5-40℃ or on rainy days.
- Storage method: Store in a cool and dry place. Unopened products can be stored for one year.
Application fields of ceramic fiber blankets
High temperature thermal insulation in aerospace, steel, and petrochemical industries. Fireproof and thermal insulation for military equipment. Thermal insulation for wall linings and backings of industrial kilns and heating devices. Thermal insulation for high-temperature equipment. Thermal insulation for high-temperature pipelines. Thermal insulation and fireproofing for electrical components. High temperature gaskets. Raw materials for modules and folding blocks.







